Iterative method to solve linear system
Note: Most of the code are copied from others. Not wrtitten by me.
[]: https://docs.julialang.org/en/v1/stdlib/LinearAlgebra/ “Julia docs”
[]: https://jermwatt.github.io/machine_learning_refined/notes/16_Linear_algebra/16_5_Norms.html “norm”
Prerequisite
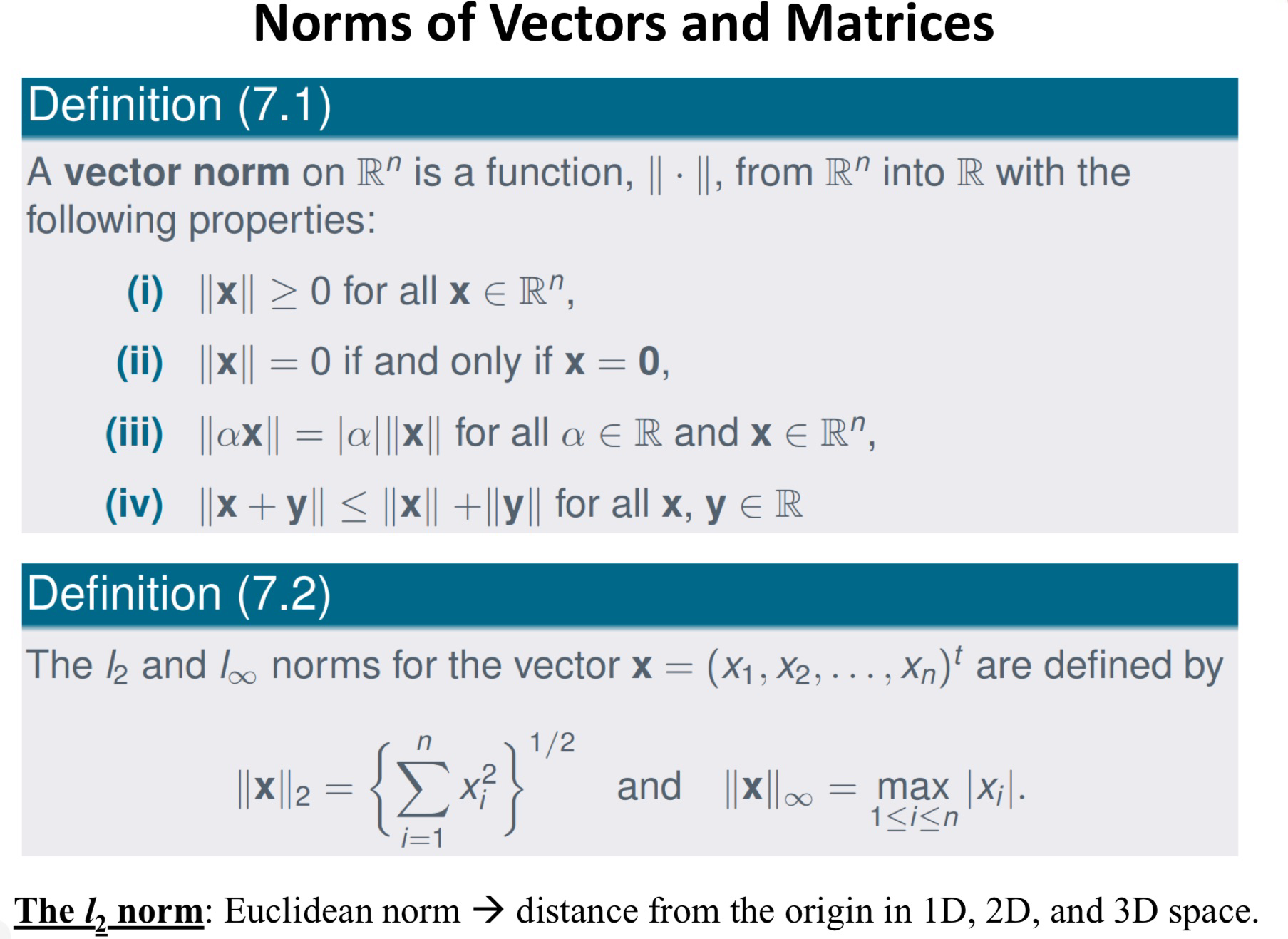
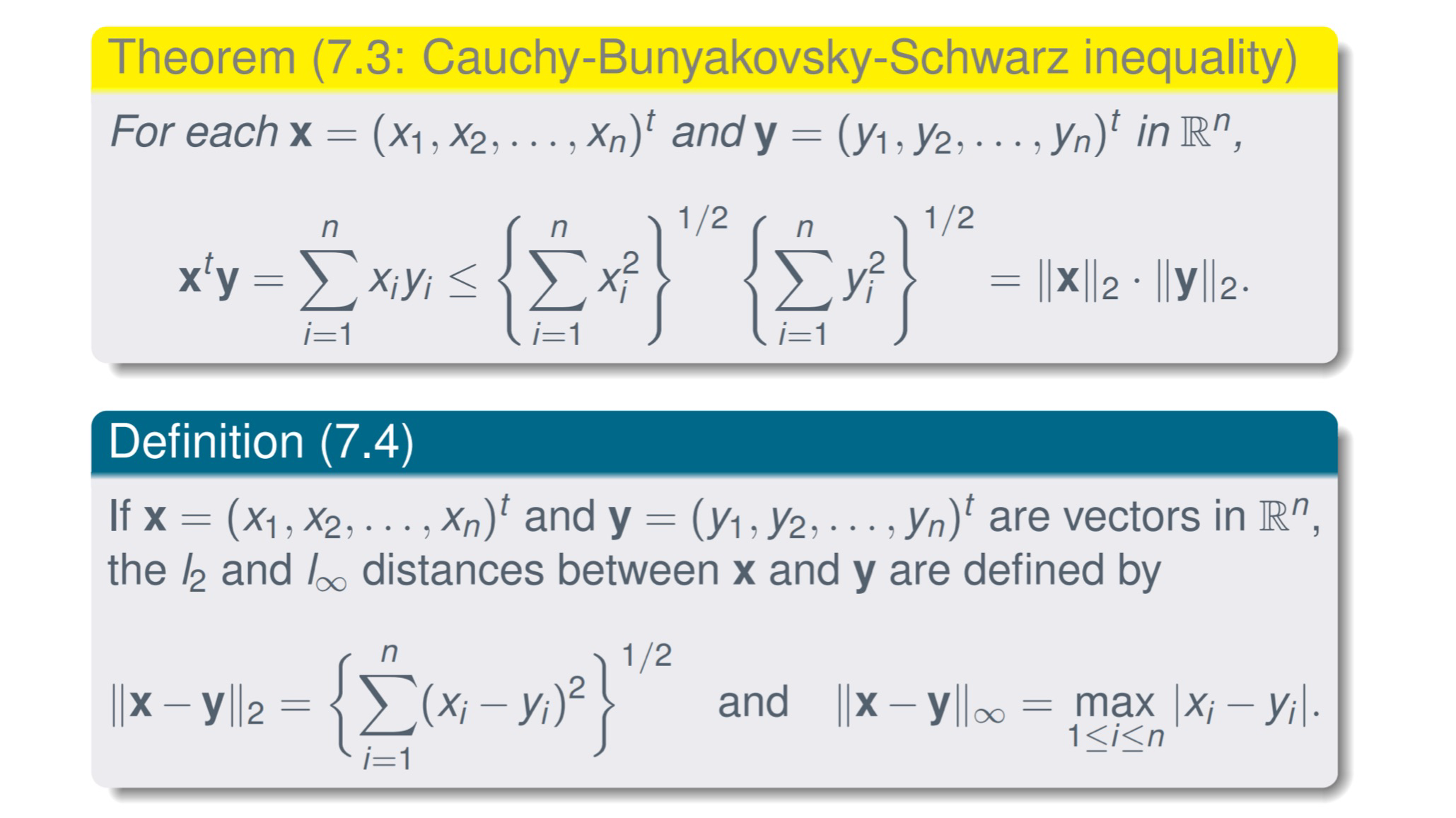
Norms of Vectors and Matrices
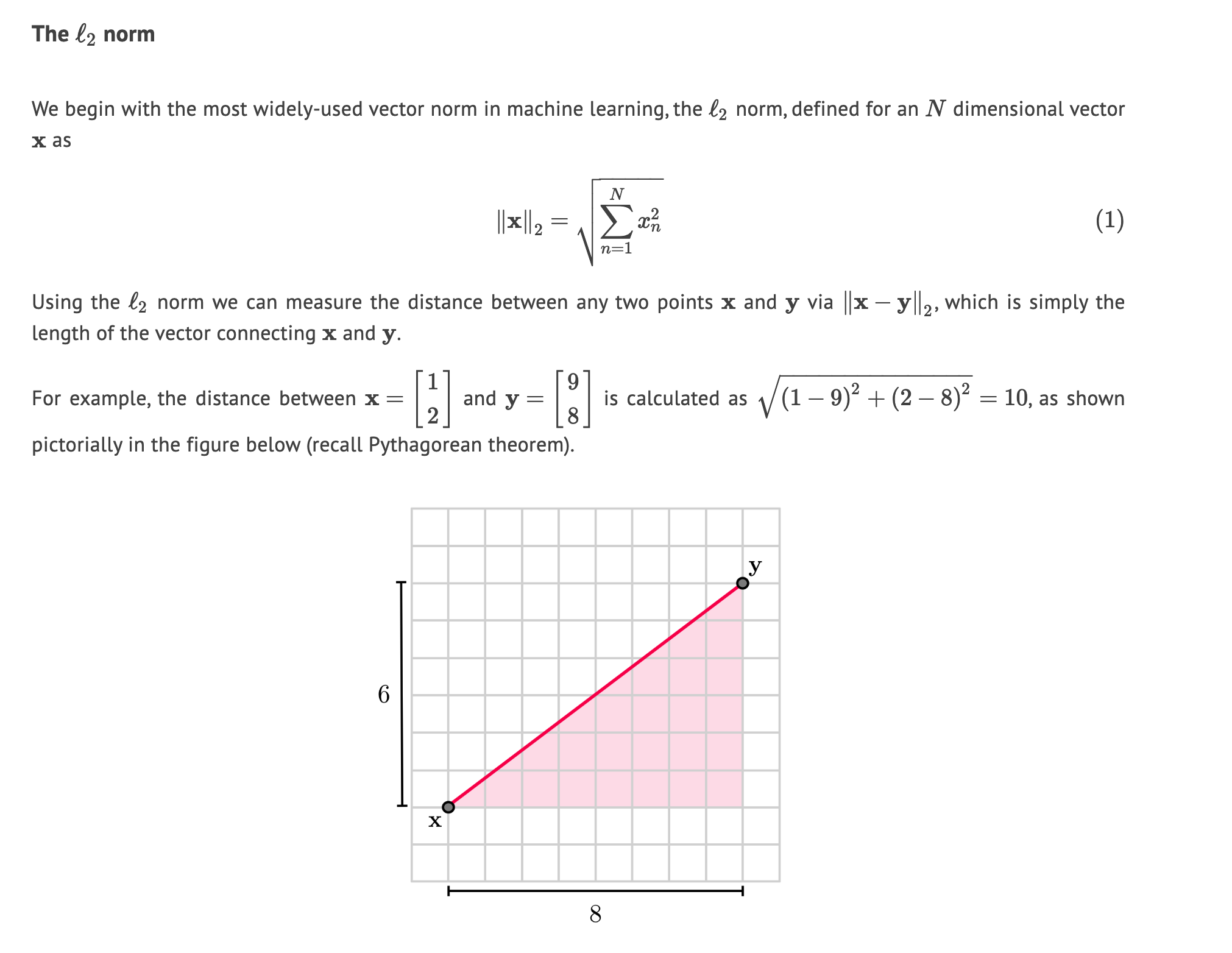
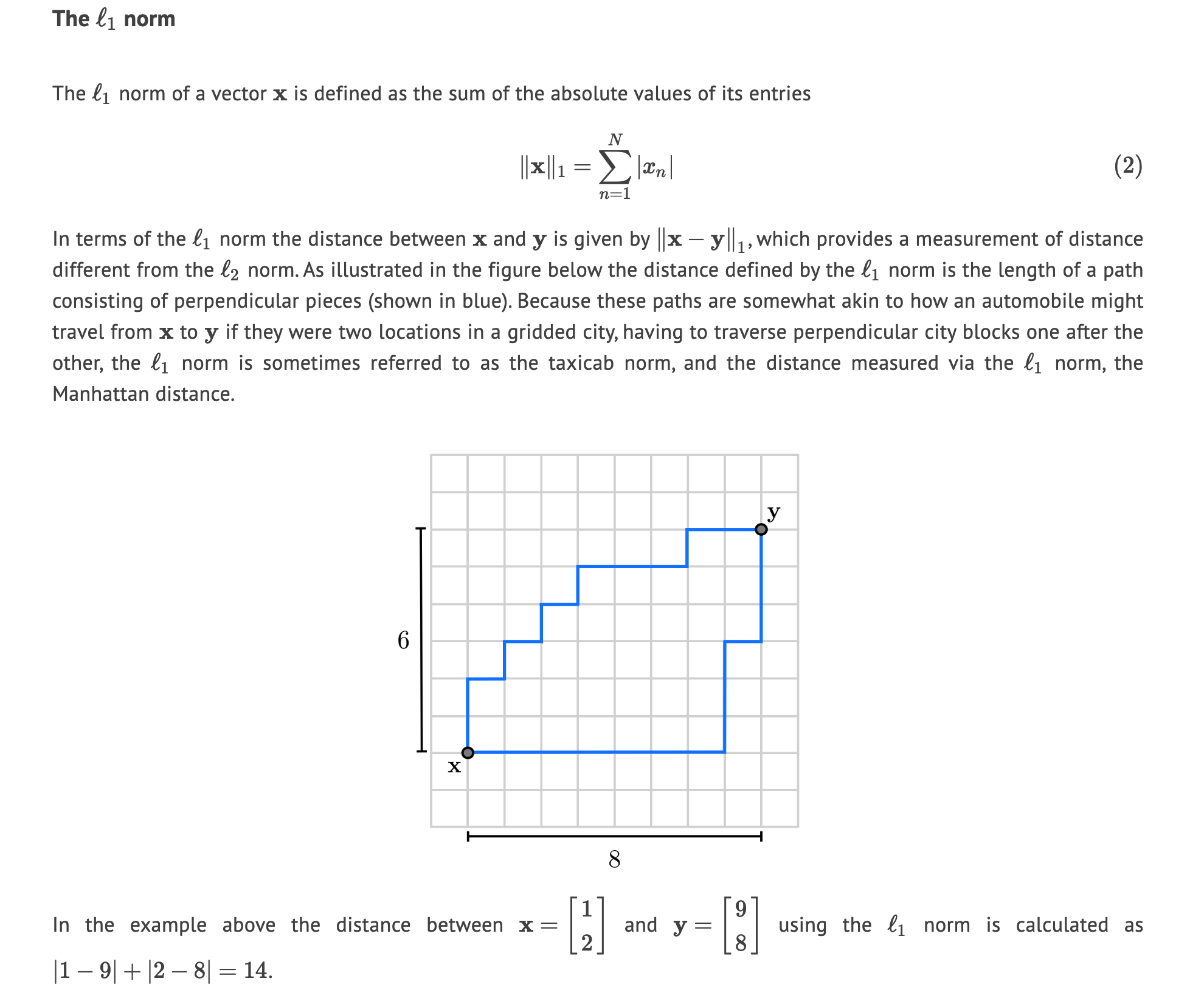
Examples
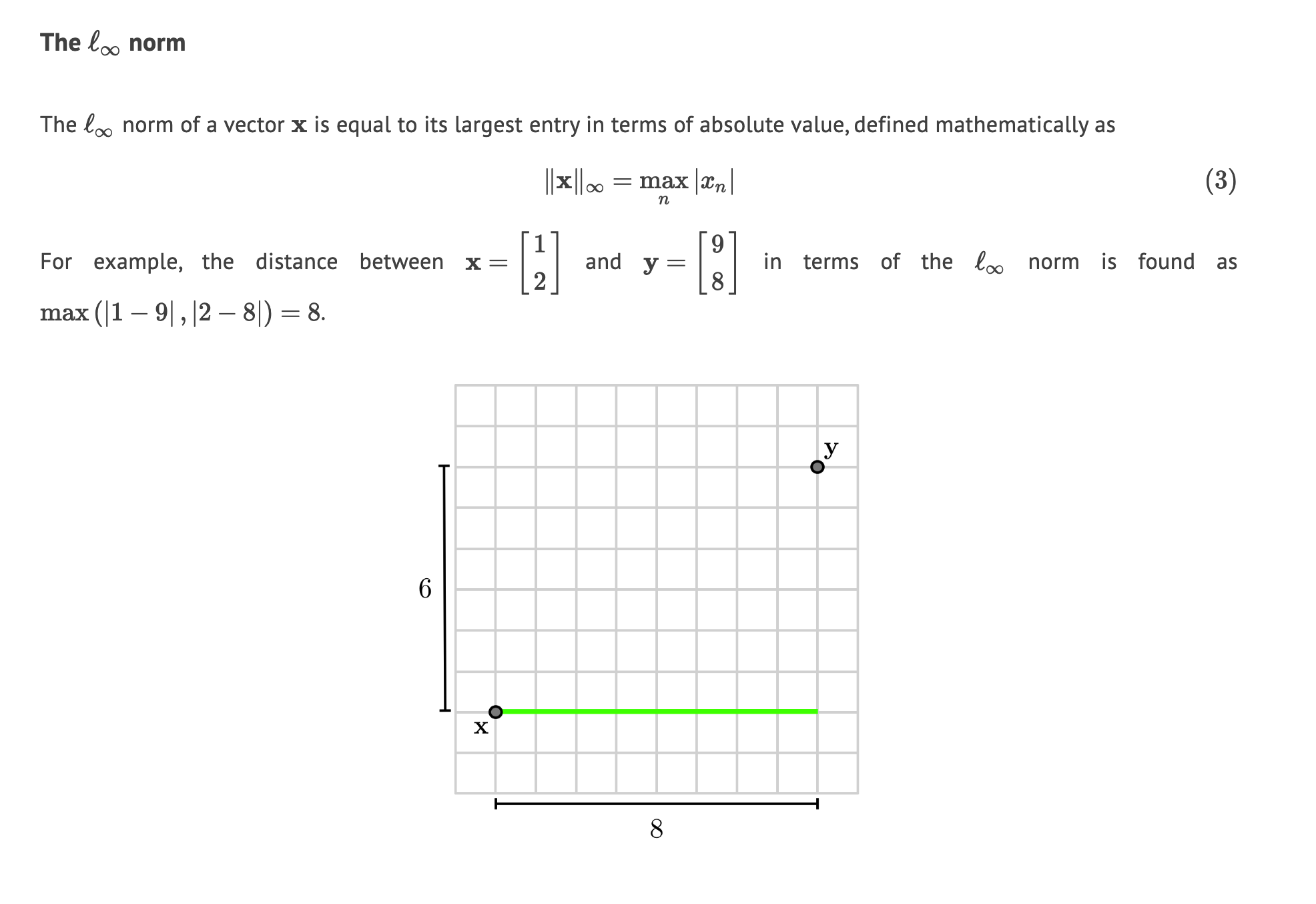

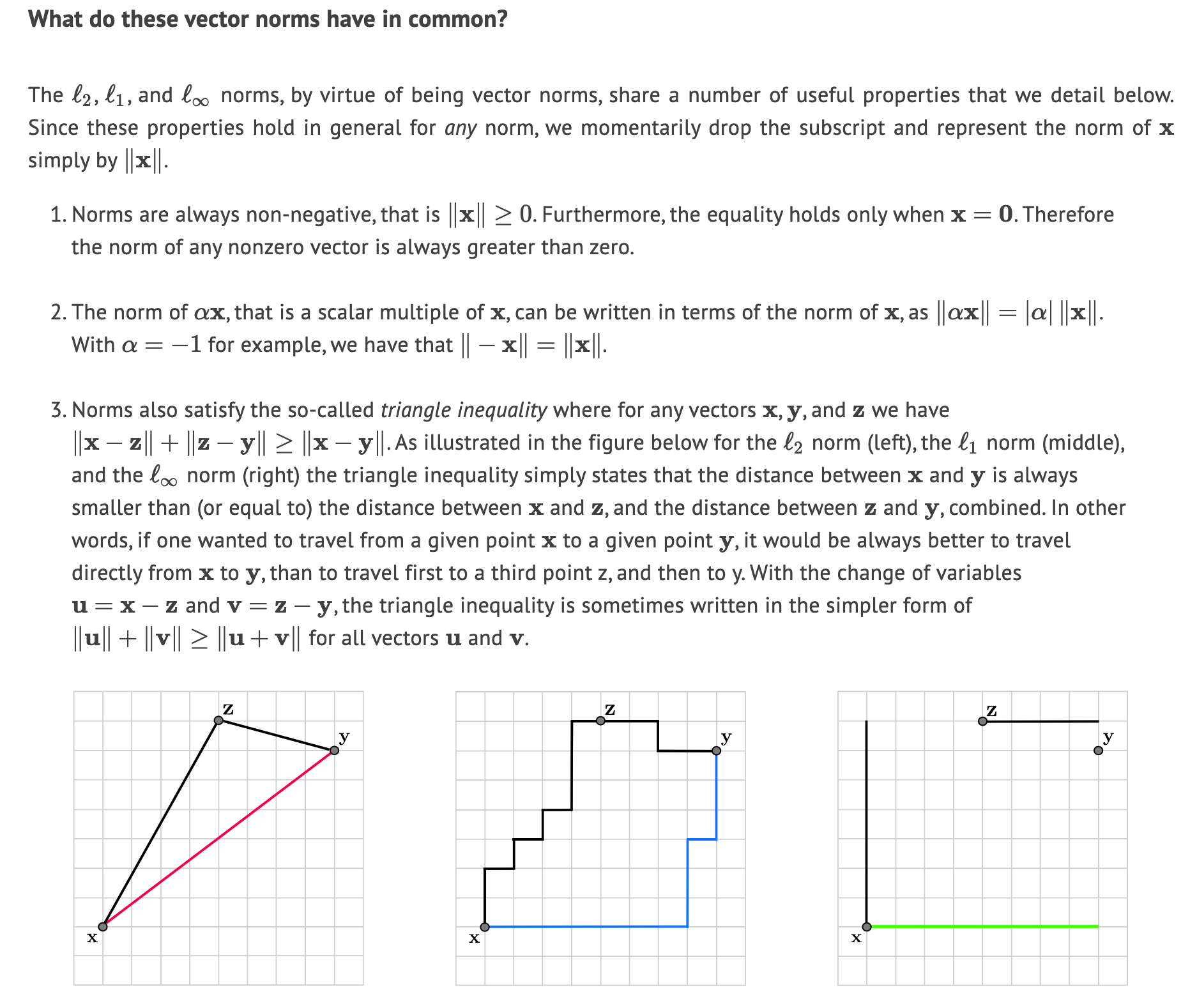
Matrix norm:

Calculate the norm:
using LinearAlgebra
A = ##input matrix/vector
println(norm(A))
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors => Spectral radius

Jacobi method
See: https://www.foopiew.com/spectral-radius-jacobi-method/
Pre: determine the spectral radius
using LinearAlgebra
A = [4 1 2; 3 5 1; 1 1 3];
D = Diagonal(A); # Diagonal matrix
R = A - D; # Off-diagonal matrix
G = -inv(D)*R; # Iteration matrix
eigenvalues=eigvals(G) # Compute the eigenvalues
spectral_radius = maximum(abs.(eigenvalues)) # Compute the spectral radius
println("Spectral Radius: ", spectral_radius)
Solve
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
# ==============================
# Jacobi linear solver algorithm
# ==============================
function jacobi_solve(A::Matrix{Float64}, b::Vector{Float64},
x0::Vector{Float64}, tol::Float64,
zeroTolerance::Float64, max_iters::Int)
# Number of unknowns
# ------------------
n = length(b)
# Check for near-zero diagonal entries
# ------------------------------------
if any(abs.(diag(A)) .< zeroTolerance)
error("Near-zero diagonal entry found in the matrix.")
end
# Solution vector initialisation
# ------------------------------
x = copy(x0)
x_new = zeros(n)
# Plot vector initialisation
# --------------------------
errors = Float64[]
# Perform iteration
# -----------------
for iter = 1:max_iters
# Loop rows
for i = 1:n
x_new[i] = (b[i] - dot(A[i, :], x) + A[i, i] * x[i]) / A[i, i]
end
# Evaluate error
err = norm(x_new - x)
push!(errors, err) # Store the current error
# Check for convergence
if err < tol
return x_new, iter, errors
end
# Update the solution vector
x .= x_new
end
error("Maximum number of iterations reached without convergence.")
end
# =============
# Problem setup
# =============
# A = [4.0 1.0 2.0; 3.0 5.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 3.0]
# b = [1.0; -2.0; 0.0]
## the following matrix is from the turorial
A = [3.0 1.0 -1.0; 2.0 4.0 1.0; -1.0 2.0 5.0];
b = [4.0; 1.0; 1.0]
x0 = zeros(length(b)) # Initial guess for solution vector
# ==================
# Numerical settings
# ==================
tolerance = 1E-8
zeroTolerance = 1E-12
iterMax = 500
# =====
# Solve
# =====
try
x, niter, errors = jacobi_solve(A, b, x0, tolerance, zeroTolerance, iterMax)
println("Converged in $niter iterations. Solution: $x")
# Plotting error vs iteration number
plot(1:niter, errors, yscale=:log10, xlabel="Iteration Number", ylabel="Error (log scale)", title="Convergence of Jacobi Method", legend=false, line=:line, marker=:circle)
catch error
println(error)
end
Gauss Seidel method
See:https://www.foopiew.com/linear-solver-gauss-seidel-method/
Pre: determine the spectral radius
## for computing the spectral radius
using LinearAlgebra
A = [4 1 2; 3 5 1; 1 1 3];
D = Diagonal(A); # Diagonal part
L = tril(A, -1); # Strictly lower triangle part
U = triu(A, 1); # Strictly upper triangle part
G = -inv(L+D)*U; # Iteration Matrix
eigenvalues=eigvals(G) # Compute the eigenvalues
spectral_radius = maximum(abs.(eigenvalues)) # Compute the spectral radius
println("Spectral Radius: ", spectral_radius)
Solve
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
# ====================================
# Gauss-Seidel linear solver algorithm
# ====================================
function gauss_seidel_solve(A::Matrix{Float64}, b::Vector{Float64}, x0::Vector{Float64}, tol::Float64, zeroTolerance::Float64, max_iters::Int)
# Number of unknowns
# ------------------
n = length(b)
# Check for near-zero diagonal entries
# ------------------------------------
if any(abs.(diag(A)) .< zeroTolerance)
error("Near-zero diagonal entry found in the matrix.")
end
# Solution vector initialisation
# ------------------------------
x = copy(x0)
# Plot vector initialisation
# --------------------------
errors = Float64[]
# Perform iteration
# -----------------
for iter = 1:max_iters
x_old = copy(x)
# Loop rows
for i = 1:n
sum1 = dot(A[i, 1:i-1], x[1:i-1])
sum2 = dot(A[i, i+1:end], x_old[i+1:end])
x[i] = (b[i] - sum1 - sum2) / A[i, i]
end
# Evaluate error
err = norm(x - x_old)
push!(errors, err) # Store the current error
# Check for convergence
if err < tol
return x, iter, errors
end
end
error("Maximum number of iterations reached without convergence.")
end
# =============
# Problem setup
# =============
# A = [4 1 2; 3 5 1; 1 1 3];
# b = [1.0; -2.0; 0.0]
A = [3 1 -1; 2 4 1; -1 2 5];
b = [4.0; 1.0; 1.0]
# Processing matrix and vectors
A = convert(Matrix{Float64}, A) # Ensure they are not integers
x0 = zeros(length(b)) # Initial guess for solution Vector
# ==================
# Numerical settings
# ==================
tolerance = 1E-8
zeroTolerance = 1E-12
iterMax = 500
# =====
# Solve
# =====
try
x, niter, errors = gauss_seidel_solve(A, b, x0, tolerance, zeroTolerance, iterMax)
println("Converged in $niter iterations. Solution: $x")
# Plotting error vs iteration number
plot(1:niter, errors, yscale=:log10, xlabel="Iteration Number", ylabel="Error (log scale)", title="Convergence of Gauss-Seidel Method", legend=false, line=:line, marker=:circle, xticks=1:niter)
catch error
println(error)
end
Successive over-relaxation method
See:https://www.foopiew.com/linear-solver-successive-over/
1
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
# ==================================================
# Successive over-relaxation linear solver algorithm
# ==================================================
function SOR_solve(A::Matrix{Float64}, b::Vector{Float64}, x0::Vector{Float64}, ω::Float64, tol::Float64, zeroTolerance::Float64, max_iters::Int)
# Number of unknowns
# ------------------
n = length(b)
# Check for near-zero diagonal entries
# ------------------------------------
if any(abs.(diag(A)) .< zeroTolerance)
error("Near-zero diagonal entry found in the matrix.")
end
# Solution vector initialisation
# ------------------------------
x = copy(x0)
# Plot vector initialisation
# --------------------------
errors = Float64[]
# Perform iteration
# -----------------
for iter = 1:max_iters
x_old = copy(x)
# Loop rows
for i = 1:n
sum1 = dot(A[i, 1:i-1], x[1:i-1])
sum2 = dot(A[i, i+1:end], x_old[i+1:end])
x[i] = (1-ω)*x[i] + ω*(b[i] - sum1 - sum2) / A[i, i]
end
# Evaluate error
err = norm(x - x_old)
push!(errors, err) # Store the current error
# Check for convergence
if err < tol
return x, iter, errors
end
end
error("Maximum number of iterations reached without convergence.")
end
# =============
# Problem setup
# =============
A = [4 1 2; 3 5 1; 1 1 3];
b = [1.0; -2.0; 0.0]
# Processing matrix and vectors
A = convert(Matrix{Float64}, A) # Ensure they are not integers
x0 = zeros(length(b)) # Initial guess for solution Vector
# ==================
# Numerical settings
# ==================
ω=1.05
tolerance = 1E-8
zeroTolerance = 1E-12
iterMax = 500
# =====
# Solve
# =====
try
x, niter, errors = SOR_solve(A, b, x0, ω, tolerance, zeroTolerance, iterMax)
println("Converged in $niter iterations. Solution: $x")
# Plotting error vs iteration number
plot(1:niter, errors, yscale=:log10, xlabel="Iteration Number", ylabel="Error (log scale)", title="Convergence of SOR Method", legend=false, line=:line, marker=:circle)
catch error
println(error)
end
2
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
# ==================================================
# Successive over-relaxation linear solver algorithm
# ==================================================
function SOR_solve(A::Matrix{Float64}, b::Vector{Float64},
x0::Vector{Float64}, ω::Float64, tol::Float64,
zeroTolerance::Float64, max_iters::Int)
# Number of unknowns
# ------------------
n = length(b)
# Check for near-zero diagonal entries
# ------------------------------------
if any(abs.(diag(A)) .< zeroTolerance)
error("Near-zero diagonal entry found in the matrix.")
end
# Solution vector initialisation
# ------------------------------
x = copy(x0)
# Plot vector initialisation
# --------------------------
errors = Float64[]
# Perform iteration
# -----------------
for iter = 1:max_iters
x_old = copy(x)
# Loop rows
for i = 1:n
sum1 = dot(A[i, 1:i-1], x[1:i-1])
sum2 = dot(A[i, i+1:end], x_old[i+1:end])
x[i] = (1-ω)*x[i] + ω*(b[i] - sum1 - sum2) / A[i, i]
end
# Evaluate error
err = norm(x - x_old)
push!(errors, err) # Store the current error
# Check for convergence
if err < tol
return x, iter, errors
end
end
error("Maximum number of iterations reached without convergence.")
end
# =============
# Problem setup
# =============
A = [4 1 2; 3 5 1; 1 1 3];
b = [1.0; -2.0; 0.0]
# Processing matrix and vectors
A = convert(Matrix{Float64}, A) # Ensure they are not integers
x0 = zeros(length(b)) # Initial guess for solution Vector
# ==================
# Numerical settings
# ==================
tolerance = 1E-8
zeroTolerance = 1E-12
iterMax = 500
# =====
# Solve
# =====
ω_list = range(start=0.1, step=0.05, stop=1.6)
niter_list = Float64[]
for iω in eachindex(ω_list)
ω=ω_list[iω]
try
x, niter, errors = SOR_solve(A, b, x0, ω, tolerance, zeroTolerance, iterMax)
println("Converged in $niter iterations. Solution: $x")
push!(niter_list, niter) # Store the number of iterations to converge
catch error
println(error)
end
end
# Plot ω-niter
plot(ω_list, niter_list, xlabel="Relaxation Factor \\omega", ylabel="Number of Iterations to Converge", title="Effect of \\omega in SOR Method", legend=false, line=:line, marker=:circle)

